
Brian Laundrie’s mom vowed to help him ‘dispose of body’ in letter before his trip with Gabby Petito
The letter sparked fury from Petito's parents, who insist it is evidence Roberta Laundrie plotted with her son to cover up their daughter's murder
2023-05-25 20:48

Biden treads tightrope on Israel-Hamas ceasefire
US President Joe Biden’s administration is treading a tightrope on Israel, with Washington firmly backing its ally while urging caution and calling for pauses in the...
2023-10-25 06:47

'Walking Dead' spinoffs, 'Interview With the Vampire' can resume with actors' union approval
Two spinoffs of “The Walking Dead” and the next season of “Interview With the Vampire” will be resuming production despite the Hollywood strikes after reaching a deal with the actors' union
2023-09-01 08:51

What happened between Logan Paul and KSI? Fitness influencer once vowed to 'kill' his boxing rival: 'I am going to light you on fire'
Logan Paul said, 'The circumstance I’m about to describe is one of the most interesting phenomenons I’ve ever seen online'
2023-08-20 13:54

Palestinians haunted by 'Nakba' while bracing for Gaza offensive
By Nidal al-Mughrabi GAZA When Israel told residents of Gaza to leave their homes in the densely populated
2023-10-15 07:49

Guardsman Jack Teixeira, Pentagon leak suspect, due back in court as judge weighs detention
A judge is poised to decide whether a Massachusetts Air National Guard member accused of leaking highly classified military documents will remain behind bars while he awaits trial
2023-05-19 12:23

Exclusive: DHS investigating whether floor plans and other security information were exposed in ransomware attack on contractor
Senior Department of Homeland Security officials are working to determine if a ransomware attack on government contractor Johnson Controls International has compromised sensitive physical security information such as DHS floor plans, according to internal DHS correspondence reviewed by CNN.
2023-09-29 06:19

Supreme Court strikes down Biden’s plan to cancel student loan debts
The US Supreme Court has struck down President Joe Biden’s plan to cancel student loan debts for millions of Americans, reversing his campaign-trail promise as borrowers prepare to resume payments this summer. Chief Justice John Roberts delivered the 6-3 decision from the court’s conservative majority on 30 June. The ruling, which stems from a pair of cases challenging the Biden administration and the US Department of Education, argues that the president does not have the authority to implement sweeping relief, and that Congress never authorised the administration to do so. Within 30 minutes on the last day of its term, the court upended protections for LGBT+ people and blocked the president from a long-held promise to cancel student loan balances amid a ballooning debt crisis impacting millions of Americans. Under the plan unveiled last year, millions of people who took out federally backed student loans would be eligible for up to $20,000 in relief. Borrowers earning up to $125,000, or $250,000 for married couples, would be eligible for up to $10,000 of their federal student loans to be wiped out. Those borrowers would be eligible to receive up to $20,000 in relief if they received Pell grants. Roughly 43 million federal student loan borrowers would be eligible for that relief, including 20 million people who stand to have their debts canceled completely, according to the White House. Roughly 16 million already submitted their applications and received approval for debt cancellation last year, according to the Biden administration. The long-anticipated plan for debt cancellation was met almost immediately with litigation threats from conservative legal groups and Republican officials, arguing that the executive branch does not have authority to broadly cancel such debt. Six GOP-led states sued the Biden administration to stop the plan altogether, and a federal appeals court temporarily blocked any such relief as the legal challenges played out. Lawyers for the Biden administration contended that he has the authority to broadly cancel student loan debt under the Higher Education Relief Opportunities for Students Act of 2003, which allows the secretary of education to waive or modify loan provisions following a national emergency – in this case, Covid-19. Justice Roberts wrote that the law allows the secretary to “waive or modify” existing provisions for financial assistance, “not to rewrite that statute from the ground up.” The Supreme Court’s final decision of its 2022-2023 term also comes one day after another major education ruling, as the same conservative majority upended decades of precedent intended to promote racially diverse college campuses, what civil rights groups and the court’s liberal justices have derided as the court’s perversion of the 14th Amendment and the foundational concept of equal protection. Moments before its decision in the student debt plan, the Supreme Court decided a case involving a website designer who refused to cater to same-sex couples, but the case did not involve any such couple. Likewise, the case at the centre of the court’s decision on student loans involved an independent loan servicer in Missouri that did not want to be associated with the lawsuit. The six GOP-led states that led the challenge – Arkansas, Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, Nebraska, and South Carolina – opposed the Biden administration’s plan for a range of reasons that amount to “just general grievances; they do not show the particularized injury needed to bring suit,” Justice Elena Kagan wrote in her dissent. “And the States have no straightforward way of making that showing – of explaining how they are harmed by a plan that reduces individual borrowers’ federal student-loan debt,” she added. “So the States have thrown no fewer than four different theories of injury against the wall, hoping that a court anxious to get to the merits will say that one of them sticks.” She admonished a decision in which “the result here is that the Court substitutes itself for Congress and the Executive Branch in making national policy about student-loan forgiveness.” “The Court acts as though it is an arbiter of political and policy disputes, rather than of cases and controversies,” and by deciding the case, the court exceeds “the permissible boundaries of the judicial role,” Justice Kagan wrote. Since March 2020, with congressional passage of the Cares Act, monthly payments on student loan debt have been frozen with interest rates set at zero per cent. That Covid-19-pandemic era moratorium, first enacted under Donald Trump and extended several times, was paused a final time late last year – until the Education Department is allowed to cancel debts under the Biden plan, or until the litigation is resolved, but no later than 30 June. Payments would then resume 60 days later. The amount of debt taken out to support student loans for higher education costs has surged within the last decade, alongside growing tuition costs, increased private university enrollment, stagnant wages and GOP-led governments stripping investments in higher education and aid, putting the burden of college costs largely on students and their families. The crisis has exploded to a total balance of nearly $2 trillion, mostly wrapped up in federal loans. Millions of Americans also continue to tackle accrued interest without being able to chip away at their principal balances, even years after graduating, or have been forced to leave their colleges or universities without obtaining a degree at all while still facing loan repayments. Borrowers also have been trapped by predatory lending schemes with for-profit institutions and sky-high interest rates that have made it impossible for many borrowers to make any progress toward paying off their debt, with interest adding to balances that exceed the original loan. One analysis from the Education Department found that nearly 90 per cent of student loan relief would support people earning less than $75,000 per year. The median income of households with student loan balances is $76,400, while 7 per cent of borrowers are below the poverty line. That debt burden also falls disproportionately on Black borrowers and women. Black college graduates have an average of $52,000 in student loan debt and owe an average of $25,000 more than white graduates, according to the Education Data Initiative. Four years after graduating, Black student loan borrowers owe an average of 188 per cent more than white graduates. Women borrowers hold roughly two-thirds of all student loan debt, according to the American Association of University Women. Mr Biden’s announcement fulfilled a campaign-trail pledge to wipe out $10,000 in student loan debt per borrower if elected, though debt relief advocates and progressive lawmakers have urged him to cancel all debts and reject means-testing barriers in broad relief measures. In November 2020, the president called on Congress to “immediately” provide some relief for millions of borrowers saddled by growing debt. “[Student debt is] holding people up,” he said at the time. “They’re in real trouble. They’re having to make choices between paying their student loan and paying the rent.” ReNika Moore, director of the Racial Justice Program with the ACLU, among civil rights groups that filed briefs with the Supreme Court to defend the loan cancellation plan, said the “one-two punch” to end affirmative action and block debt relief will lock Americans out of economic oppurtunity and worsen wealth equality. “We urge the Biden administration and the Department of Education to move quickly to explore other pathways to ease the debt load on student loan borrowers once payments resume after a pandemic-related pause, including new executive action under the Higher Education Act, a law that allows for student loan relief for certain groups,” she added. Read More Supreme Court allows Colorado designer to deny LGBT+ customers in ruling on last day of Pride Month Biden condemns Supreme Court striking down affirmative action: ‘This is not a normal court’ Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson delivers searing civil rights lesson in dissent to affirmative action ruling The Supreme Court’s ruling on affirmative action is ugly and frustrating – but no surprise
2023-07-01 01:57
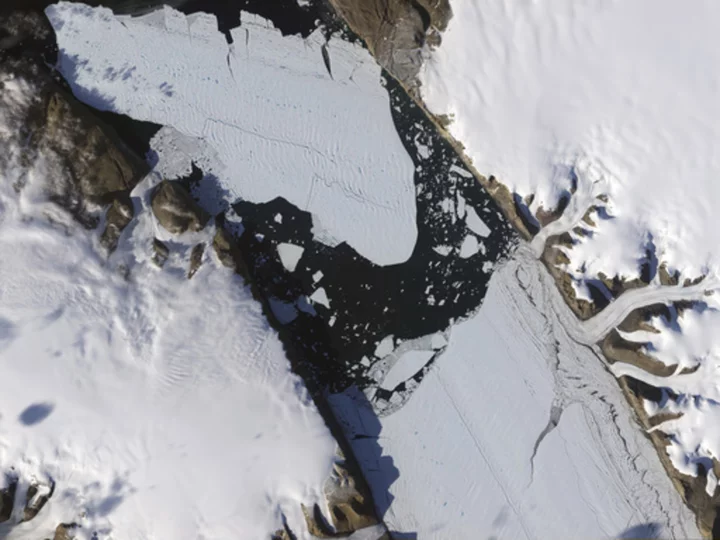

Warming-stoked tides eating huge holes in Greenland glacier
Scientists now fear increasingly warmer water in daily tides are doing much more damage to one of Greenland's glaciers than they thought
2023-05-09 03:18

UNGA Briefing: Permanent observers, more Security Council and what else is going on at the UN
It’s Day 3 of the U.N. General Assembly high-level meeting that brings world leaders together at U.N. headquarters in New York
2023-09-21 09:53

Top US senator Schumer meets Chinese foreign minister
US Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer and his delegation met with Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi on Monday...
2023-10-09 12:53
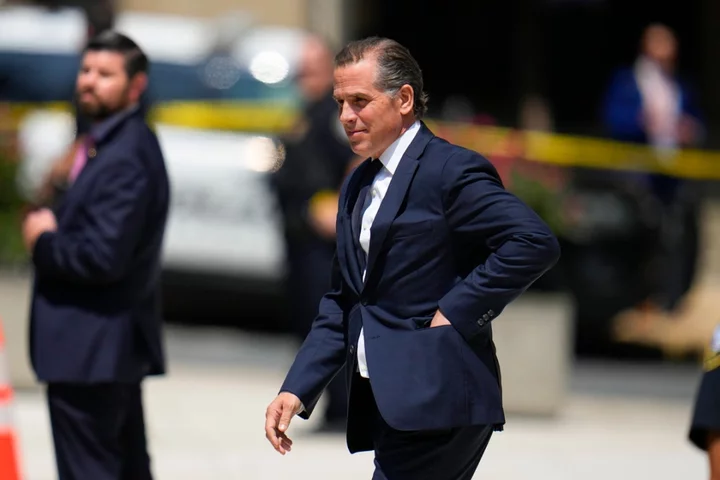

White House says Biden won’t pardon son for tax and firearms charges
The White House on Thursday said President Joe Biden would not use his authority as president to grant any pardons or other relief that would short-circuit the criminal case against his son, Hunter Biden. The younger Mr Biden, an attorney and lobbyist turned visual artist, is currently facing two misdemeanour charges for allegedly failing to pay taxes for two years, as well as a felony charge for allegedly lying on a gun background check form. During Thursday’s daily White House press briefing, press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre was asked if his father, the president, would consider pardoning his only surviving son. Ms Jean-Pierre replied: “No”. Federal prosecutors and attorneys for President Joe Biden’s son, Hunter Biden had previously settled on a deal for the lawyer and lobbyist turned artist to plead guilty to tax misdemeanour charges and enter into a diversion programme on a gun-related charge, but the judge overseeing the case demanded more information from both sides during a hearing at a Wilmington, Delaware courthouse on Wednesday. US District Judge Maryellen Noreika ordered attorneys from both sides to file briefs with the court on a provision of the diversion agreement which she had questioned because it raised separation of powers concerns, or modify the agreement to exclude the provision she questioned. The agreement, which she had reviewed, said that she would be responsible for deciding if Mr Biden was ever in breach of the agreement. She suggested that such a role would be improper for her because it is the executive branch, through prosecutors, which makes charging decision. Because Mr Biden had to enter a plea at his court appearance, he has pleaded not guilty while attorneys from both sides confer to make the agreement comply with the judge’s concerns. He will be able to enter a guilty plea when his attorneys and prosecutors have settled on language for a deal. Read More Trump slaps down reports of imminent Jan 6 grand jury indictment - live Sen Dianne Feinstein appears confused at meeting Deep dive into Meta's algorithms shows that America's political polarization has no easy fix
2023-07-28 03:26
You Might Like...
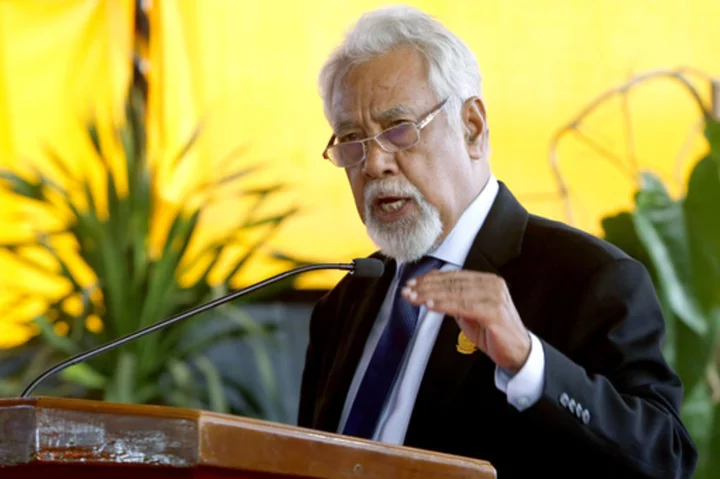

East Timor's independence hero Xanana Gusmao returns to power as prime minister

Ambient Photonics Raises $30M in Series A2 Funding: Propelling the Future of Battery-Free Connected Devices
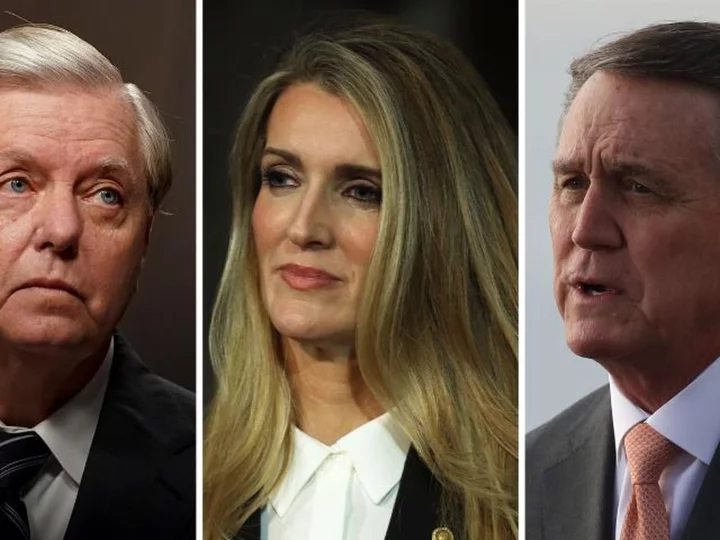

Fulton County special grand jury recommended charges against Lindsey Graham, David Perdue and Kelly Loeffler
Flat Earther claims entire continents containing 'aliens' are being kept secret

Arnold Schwarzenegger’s son Patrick impressed with Logan Paul's PRIME's growth: 'Could easily be public company'

Sneako: YouTube streamer's 5 most controversial feuds so far

'I'm always thinking about him': Jordana Brewster remembers Paul Walker as a 'wonderful good soul'

Who is Talitha Russell? Carlee Russell's mom says ‘not a good time’ to queries after daughter confesses kidnapping hoax
